3D Tools and Effects
Creating Materials
To create a new material, you can modify a default one. If any of the library materials is similar to what you want to create, start from this predesigned material.
To adjust the material properties, open the Material section in the Inspector.
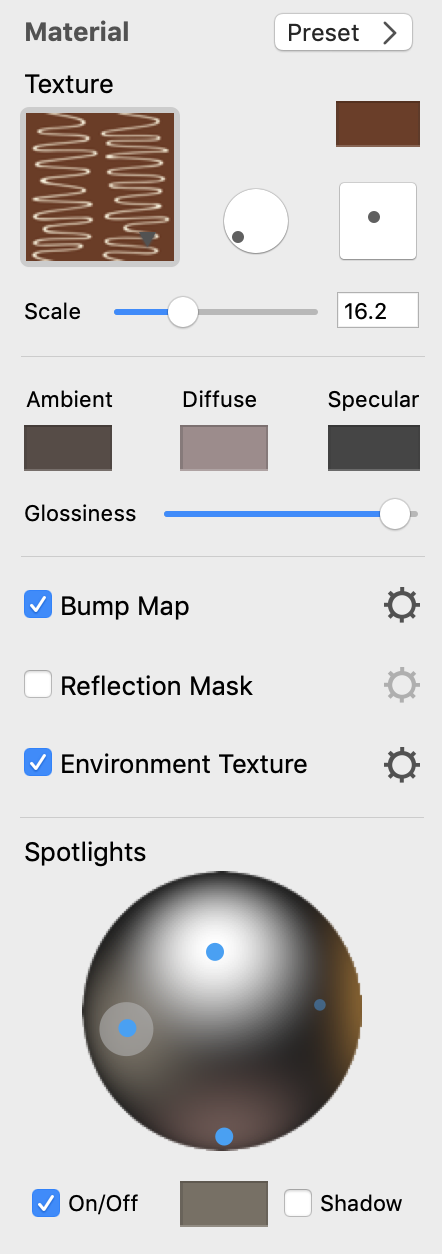
Texture
To open the texture library, click on the preview of the current texture. In the texture library, you can choose textures from one of several categories, or select a plain color at the top of the library.
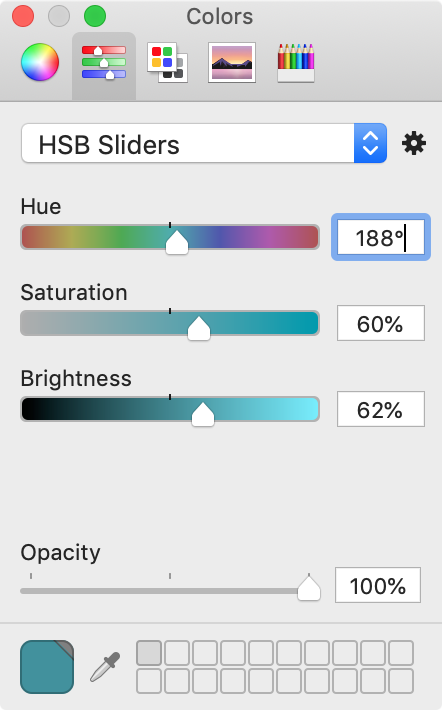
The Color button at the top right corner lets you change texture colors. Its effect is a combination of the Hue, Saturation and Brightness color properties. You can switch the Colors pane to the HSB Sliders mode to be able to adjust the sliders separately.
The round and square controls in the middle change the angle and offset of the texture.
Scale lets you magnify the texture.
Material Finish and Colors
This group of material properties is responsible for how lighting affects the object. You should adjust the parameters below together with the light sources.

Ambient, Diffuse and Specular colors let you adjust the look of shadowed and lit parts of the object. It is easier to learn how these colors appear on the object when only one light source is on, a plain color is used as a texture and the Bump Map and Environment Texture tools are deactivated.
Ambient is the object's color when there is no light at all. It can be black, or more often a darker version of the Diffuse color.
Diffuse is the object's color under diffuse light. In many cases, it coincides with the natural color of the object.
The Specular color is used to create a reflection of a direct light source. The more matt the object is, the bigger and less sharp the light spot is. To control this, use the Glossiness slider.
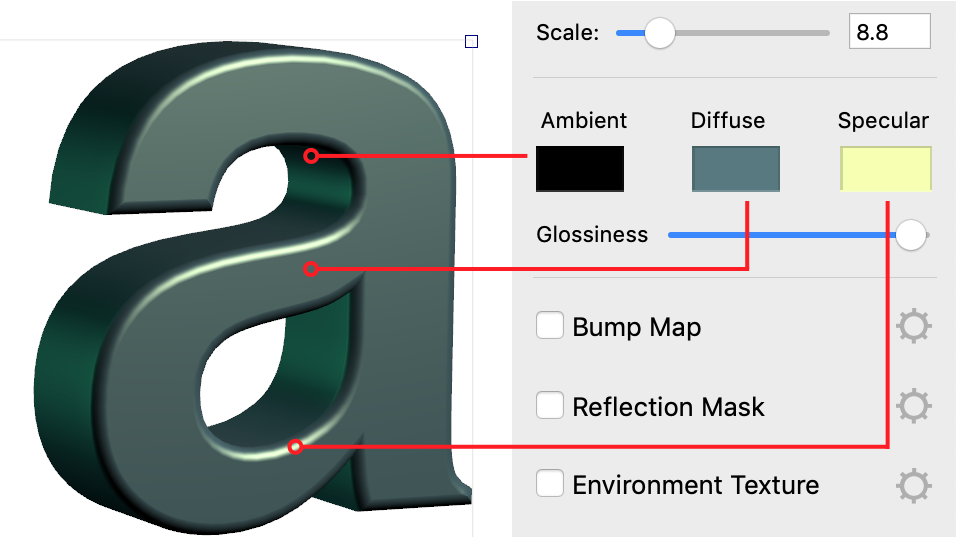
The following image shows spots on the object where the Ambient, Diffuse and Specular colors are dominant. These colors interact with each other, texture and also with applied effects. Due to this, you can see spots of pure Ambient, Diffuse and Specular colors not so often.
Glossiness makes the object look more or less glossy.
Bump Map
The Bump Map tool adds more volume to the texture details.
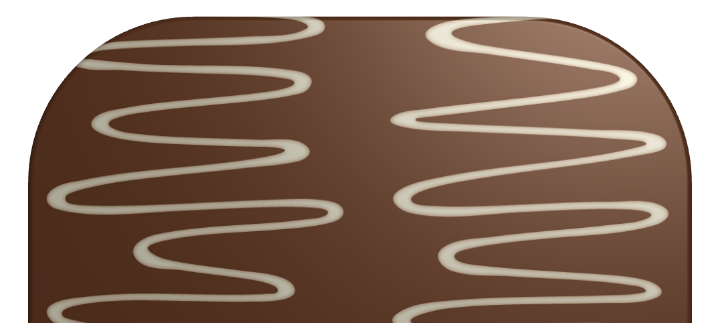
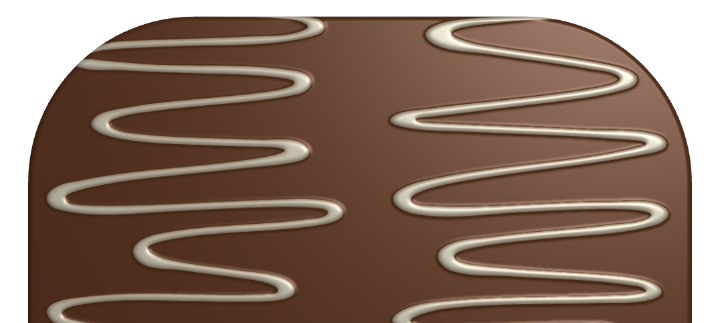
In order to select a new bump map or adjust the settings, click the corresponding gear icon.
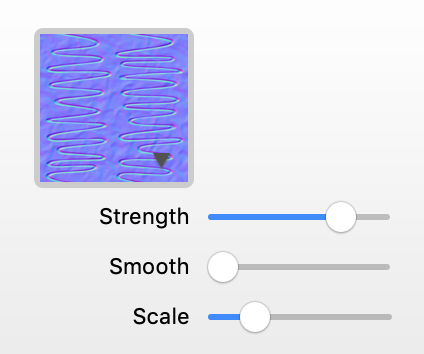
Strength controls the amount of roughness created by the tool.
Smooth makes the effect smooth by hiding smaller details.
The Scale slider lets you resize the bump map if you need to match its scale to the texture or to the object's size.
If you are using a texture from the built-in library, the program automatically finds the corresponding bump map in the library. To select a different bump map, choose one in the Bump Map settings. You need to click on the preview of the current bump map to bring up the library.
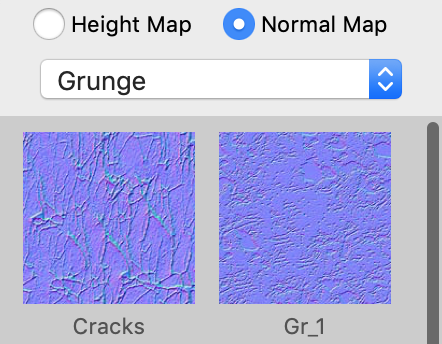
The library contains bump maps created specially for built-in textures. These bump maps add extra details to the object surface.
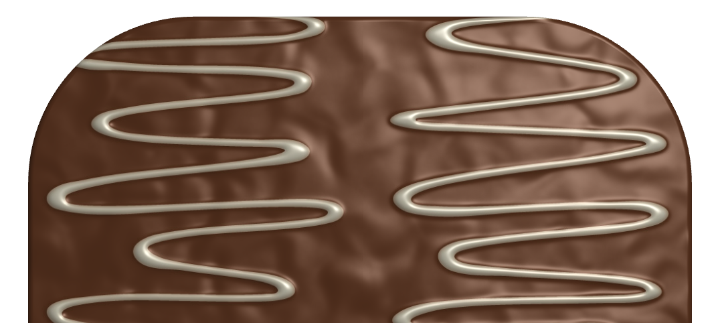
You can select one of the provided bump maps or import one from a graphic file. To do that, open the drop-down menu and choose Custom Folder…
There are two options at the top of the library: Height Map and Normal Map. They are used to specify the type of a bump map that was imported. If your bump map is a black and white image, then it is likely to be of the Height Map type. A Normal Map is usually a violet image with green and red areas. The screenshot of the library above displays examples of the Normal Map type.
Reflection Mask
Reflection masks are used to remove patches of light on the object surface. This might be useful when your 3D object should look matt.
The letter in the example below is partially covered by rust. The remains of the paint can be a bit glossy, but the rust cannot. In order to tell the program which areas shouldn't be reflective, we apply a reflection mask.
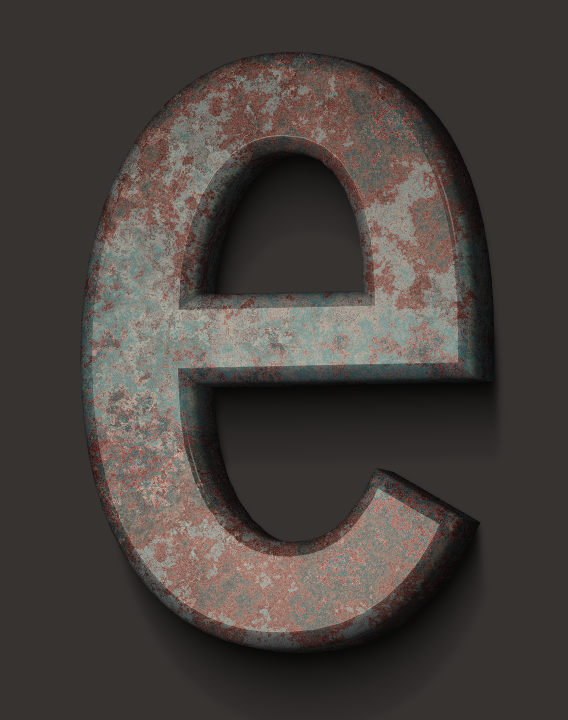
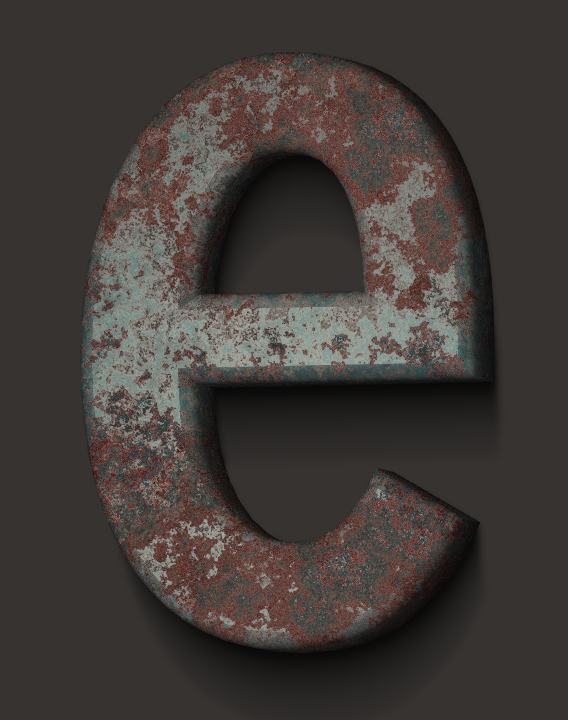
In order to change the reflection mask, click the corresponding gear icon.
If you are going to create your own reflection mask, use dark colors or black in the mask for areas where reflection should be masked.
Environment Texture
The Environment Texture tool extends the lighting effect created by the Light Sources properties. By applying an environment texture, you can simulate reflexes from particular light sources such as windows.
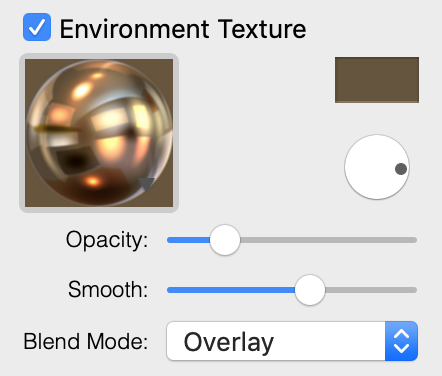
The Color button works the same way as the one in the Texture section.
A round control rotates the texture.
The Opacity parameter changes the amount of the effect applied to the object. This is useful when you need to mix the Environment Texture effect with others.
Smooth is intended to make the object matt or glossy. When you move the slider to the right, the object becomes matt.
The Blend Mode defines how the colors of the main and environment textures mix with colors of other effects.
Light Sources
The program lets you set up four light sources. In the preview, each of them is presented as a circle on a sphere. A blue circle means that the light is turned on, and a gray one indicates that the light is off. Smaller circles show the location of light sources behind the sphere.

If a light source is on, it casts light on the sphere.
You can choose the light source color in the box below the sphere.
The Shadow option allows object parts to cast shadows on the object itself. Unlike the Shadow effect in the Effects section, this option has no connection to the shadow that is cast on the background or other objects.
Saving Custom Materials
As soon as you are happy with the customized material, you can save it in the Custom category of the material library. To do this, select an object with that material applied, click the Preset button, and then click on plus at the bottom of the material library.
To rename a custom material, double-click on its name.
To delete a custom material, select it in the library and click on minus.