2D Tools and Effects
The Editor of Materials
The material editor can be accessed through the material library by choosing Shading in the Fill section. You can either create a new material or customize one of the materials in the library.
To create a new material, select Create a Material… in the drop-down list of categories.
To edit a standard or custom material, double-click on its preview. Customized and new materials will be saved in the Custom Materials category.
The window of the material editor shows a list of custom materials in the left panel. Buttons below the list let you add, remove and make a copy of the selected material. The middle part of the window shows parameters of the selected material. Samples of an applied material are displayed on the right.
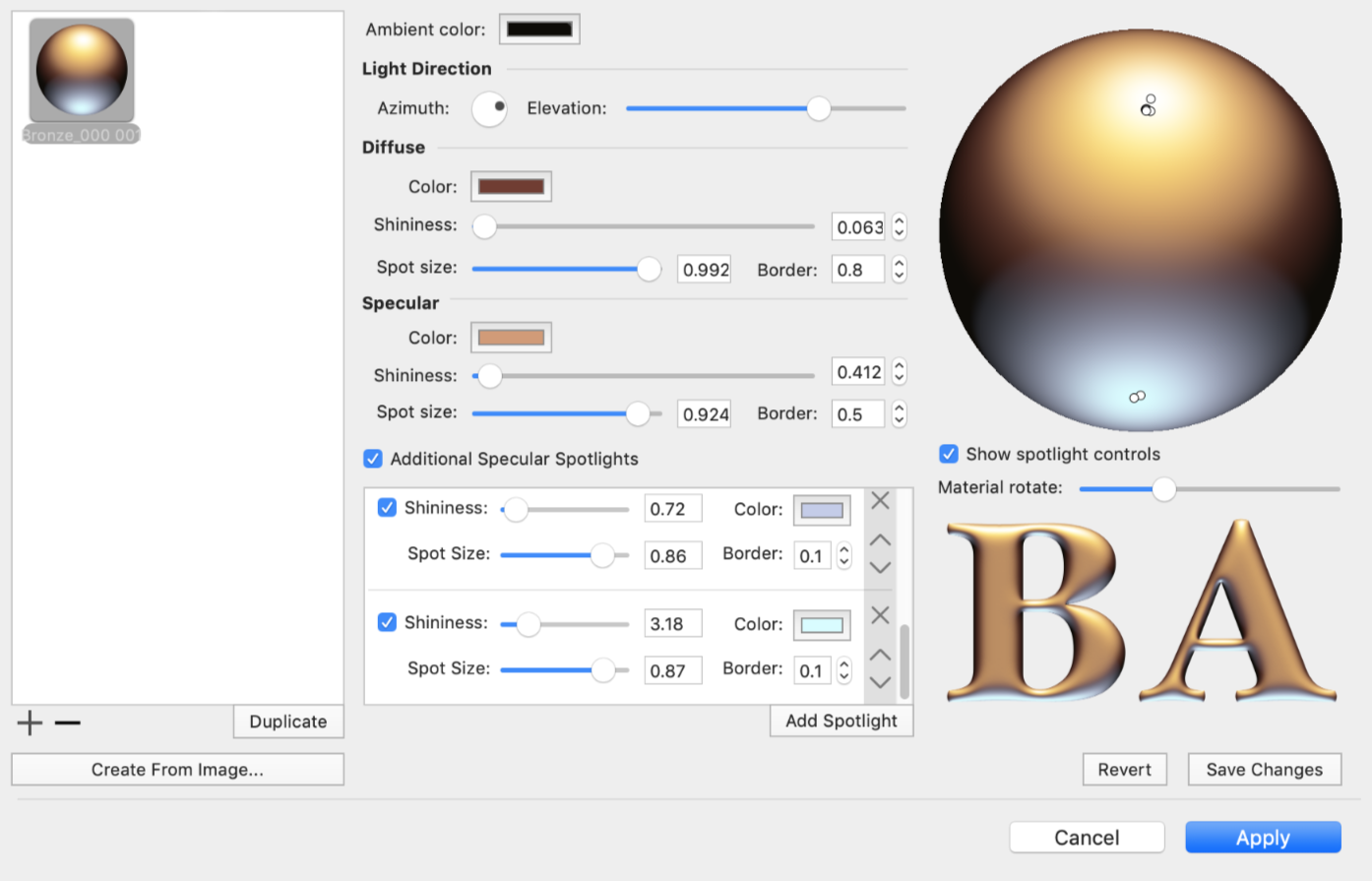
The material editor lets you create materials based on shaders and based on images.
Materials Based on Shaders
The main properties of a shader-based material are the Ambient, Diffuse and Specular colors and adjustable light sources.
The Ambient, Diffuse and Specular colors define how an object's parts look under different types of lighting. The Ambient color is the object's color in a deep shadow. The Diffuse color is the object's color in poorly dissipated white light. It's usually the natural color of the object. Finally, the Specular color lets you simulate a reflection from a light source directed to the object. One specular light source is always present (let's call it the "main" one). If necessary, you can add more.
Parameters of Light Sources
The position of each light source is displayed on the sphere as a white circle if the light is on, and a black circle if the light is off. You can move light sources by dragging the corresponding circles. If there are no circles on the sphere, select the Show spotlight controls checkbox. The main light source can also be relocated using the Azimuth and Elevation controls.
Spot Size defines the size of the reflection. Using this parameter, you can make the light be more or less directed.
Shininess blurs the light spot, making its edge more or less sharp.
Together, Spot Size and Shininess let you make the object look matte or glossy. As a rule, a reflex from the same light source is big and blurred on a matte object, and small and sharp on a glossy object.
Border controls how quickly the light fades near the edge of the light spot.
Materials Based on Images
Using images, you can create materials similar to shading materials or something completely different. An image will be mapped on the object's surface. There are no settings for image-based materials except for the possibility of rotating them.
To create a new material, click the Create from Image button and choose a graphic file. Any further adjustments can be made in the main window.